The C-TAP specification provide interfaces to different types of cards technologies (magnetic stripe, EMV smart cards with contact and contactless including applications on smartphones).
While for EMV contact cards, one EMV kernel reads all EMV cards, presently vendors will integrate multiple schemespecific contactless kernels. To reflect the merchant’s business decisions, the key element in C-TAP is dynamic recognition of multiple card brands supporting flexible and parameterized defined brand-to-acquirer associations The C-TAP application manages multiple card services and interconnects with the cards’ kernels. The application controls the interactions with the secure pin pad, the cardholder and merchant displays as well as the receipt printer.
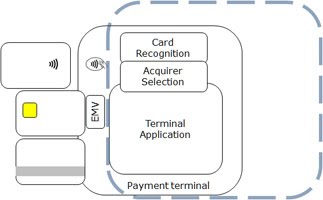
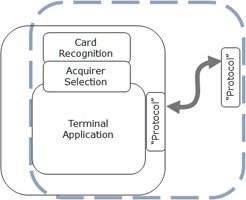
The merchant’s functionality can be driven from an Electronic Cash Register or POS configuration.
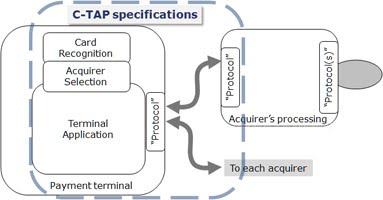
The C-TAP specification describe the messaging between terminal and acquirer.
Each acquirer can customize the transaction processing by loading its specific parameters in the terminal.
For payments, there is an exchange in 4 messages (one dialogue for authorization and one for completion).
A data dictionary drives the messaging formats. The present notation is TagLength-Value (“TLV” as for EMV). A terminal will handle multiple session with multiple acquirers, as driven by the card recognition and brand-to-acquirer associations.
A merchant can add brands to support or modify relationships with acquirers. No changes of hardware, software or configuration are required at terminal level.

Copyright (c) 2023 Acquiris, All rights reserved.